Our Services
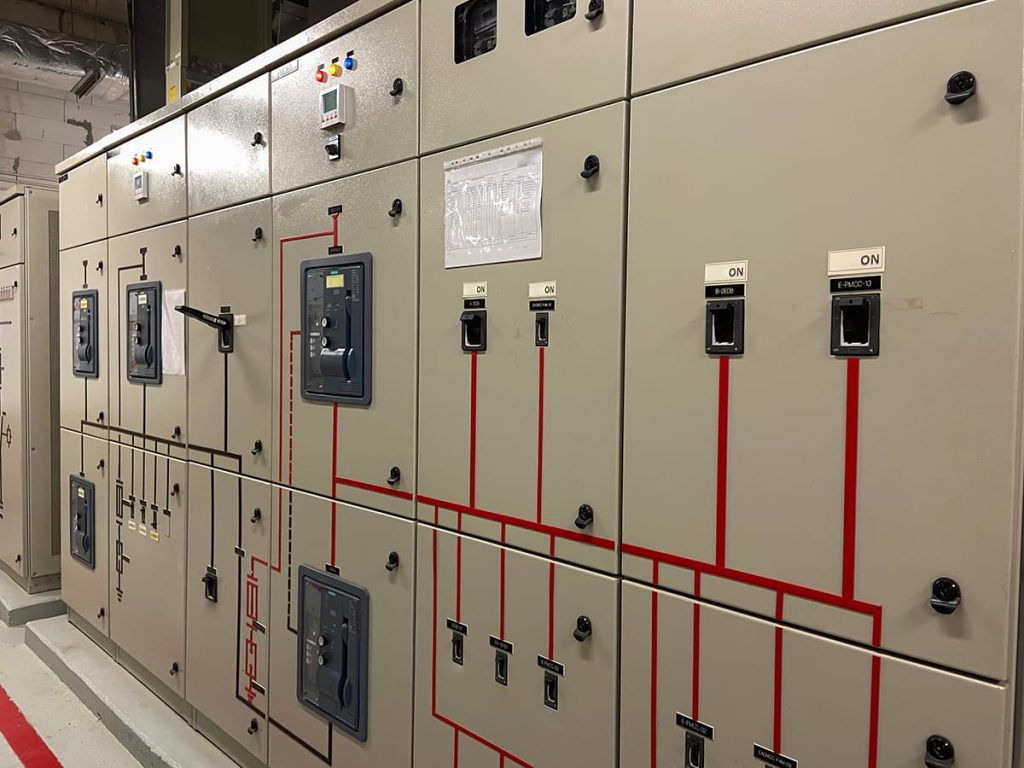

SLD
A single-line diagram (also known as an SLD or one-line diagram) is a simplified representation of an electrical system. Symbols and lines are used to represent the nodes and connections in the system, and electrical characteristics may be included as well.
In a data center, a single-line diagram is used to visualize the power distribution system to improve planning and troubleshooting, ensure redundancy, and reduce potential outages.

Electrical Layout Diagram (ELD)
Electrical layout diagram an exact graphical representation of the layout of the various fixtures, equipment, utilities, and buildings of the plant.
Types of Electrical Layout drawings
Lighting Layout
Switch gear layout
Generator and other equipment layouts
Earthing Layout
Lightning protection system layout
cable Layout
Conduit layout
cable tray layout
Area classification Layout – Hazardous Areas
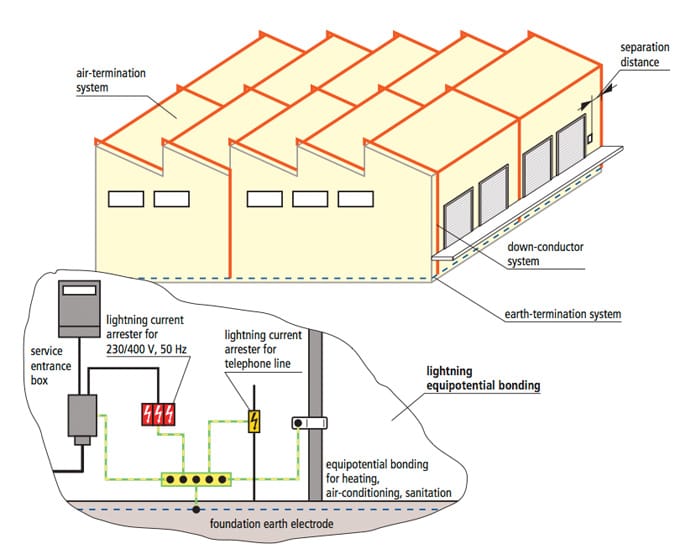
LPS
The function of a lightning protection system is to protect structures from fire or mechanical destruction and to prevent that persons in buildings are injured or even killed. An overall lightning protection system consists of external lightning protection (lightning protection/earthing) and internal lightning protection (surge protection)

Thermography scan report
Thermography is the use of an infrared imaging and measurement camera to “see” and “measure” thermal energy emitted from an object.
Thermal, or infrared energy, is light that is not visible because its wavelength is too long to be detected by the human eye; it’s the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we perceive as heat. Unlike visible light, in the infrared world, everything with a temperature above absolute zero emits heat. Even very cold objects, like ice cubes, emit infrared. The higher the object’s temperature, the greater the IR radiation emitted. Infrared allows us to see what our eyes cannot.
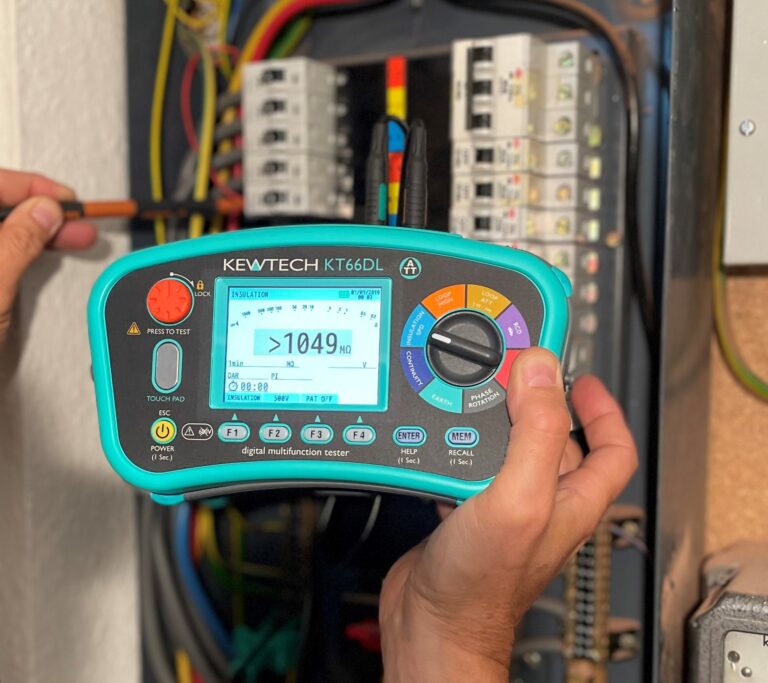
IR test
The difficulties that beset the electrical engineer are chiefly internal and invisible and they can only be effectively guarded against by “testing” or probing with electric currents. They depend chiefly on leakage, undue resistance in the conductor, and bad joints. Which lead to the waste of energy and the production of heat. These defects can only be detected by measuring, by means of special apparatus, the currents that are neither ordinary or for the purpose of testing, passed through the circuit
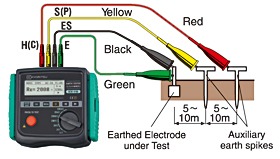
ER test
Electrical systems can fault at any time due to equipment failure, power surges caused by lightning strikes, or variations in the power grid. These faults can be hazardous for individuals handling electrical equipment, as they become an instantaneous pathway for current to flow. It’s here that the concept of proper earthing becomes crucial in preventing the fault current from entering the body or any metallic object. This blog provides a comprehensive guide on earth resistance measurement. When an earth electrode is prepared for a structure, the subsequent step involves measuring the earth resistance offered by it.
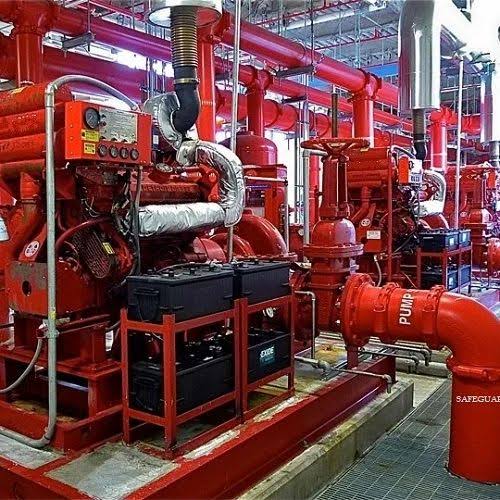

Fire Hydrant Systems
Fire hydrants are lifelines in a well-planned fire protection system. They serve as the key water source for firefighters and support the functioning of a building’s internal fire hydrants and hoses.
Put simply, they are the pillars of a fire-fighting system connected to a series of underground pipes providing water flow at crucial moments.
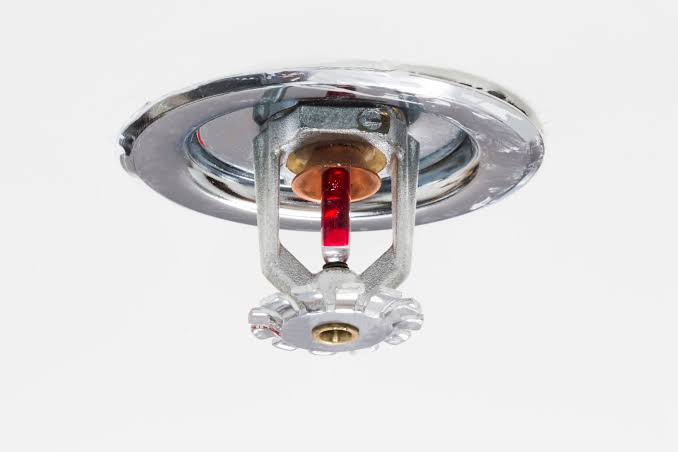

Sprinkler system:
It is a modern method of irrigation.
In this type of system, the perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals.
When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under high pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles and gets sprinkled on the crops as if it is raining.
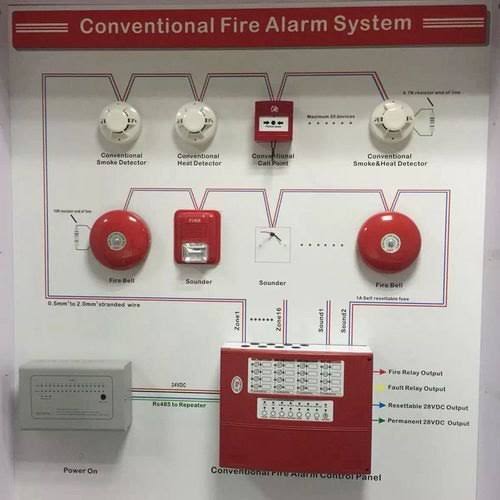

The fire detection system
The fire detection system aims to monitor for the presence of fire to alert and allow control actions to be initiated manually or automatically to minimize the likelihood of fire escalation and the probability of people being exposed and to minimize the probability of a fire condition to develop and escalate.

Substation
An electrical substation is an installation designed to establish suitable voltage levels for producing, converting, regulating, and distributing electricity.

Steam line
The meaning of STEAM LINE is a graph showing the pressure at which a liquid and its vapor are in equilibrium at any temperature.

Air compressor line
An air distribution system is designed to deliver an uninterrupted supply of compressed air right where you need it. A good air distribution piping network transports the compressed air from the source to the point-of-use in optimal conditions: with minimum pressure drop, maximum flow and the highest quality of air.
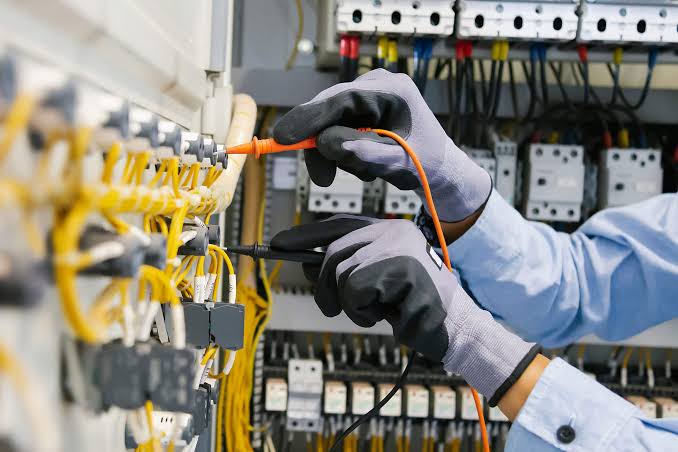

Electrical line
An electric line is a wire or conductor or associated equipment used for transmitting, transforming, or supplying electricity at a voltage greater than extra low voltage.
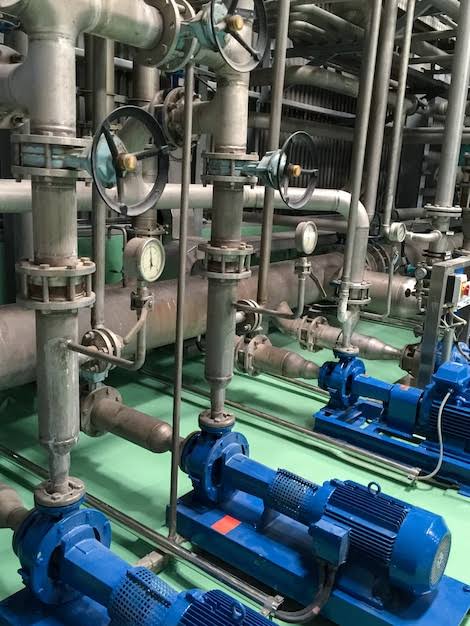

Water line
A supply line, also known as a water supply line is a metal or plastic water line that helps transfer water from the main line to essential home fixtures, including showers, sinks, and toilets.
Our Porducts

Compressor Spears

Generator Spears

Voltage stabilizer

Electronic parts

IPS

IPS

